RO vs UV: Which Water Purifier is Right for You?
Water, essential for life, comes in various forms and qualities. To ensure safe and healthy consumption, water purification has become a necessity, especially in urban areas. Two primary technologies dominate the water purification market: Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Ultraviolet (UV) purification. Let’s delve into these technologies, their pros, cons, and which one might be the best fit for your needs.
Understanding RO and UV
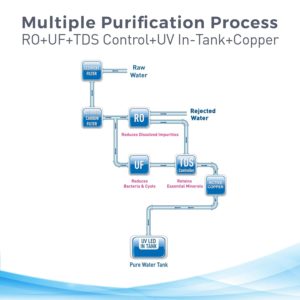
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): RO is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove contaminants from water. It effectively eliminates dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria, and viruses.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Purification: UV purification uses ultraviolet light to kill microorganisms like bacteria and viruses. It doesn’t remove dissolved solids but is highly effective in disinfecting water.
Pros and Cons of RO and UV Systems
RO Systems
- Pros:
- Removes a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved solids.
- Effective in areas with high TDS levels.
- Cons:
- Wastage of water due to the filtration process.
- Can remove essential minerals along with contaminants.
UV Systems
- Pros:
- Efficient in killing microorganisms.
- Preserves essential minerals in water.
- Low maintenance cost.
- Cons:
- Less effective in removing dissolved solids.
- Requires regular UV lamp replacement.
pH Levels and Water Purification
pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of water. The ideal pH for drinking water is between 6.5 and 8.5. While both RO and UV systems can help balance pH levels, it’s essential to check the specific purifier’s specifications to ensure it meets your needs.
TDS Levels and Water Purification
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) measure the amount of dissolved substances in water. The ideal TDS level for drinking water is below 500 ppm. A TDS meter can help you measure the TDS level in your water.
Here’s a link to a popular TDS meter on Amazon:

- Low TDS Levels (below 300 ppm): A UV purifier is sufficient.
- High TDS Levels (above 300 ppm): An RO purifier is recommended.
In-Built Tank vs. Direct Dispensers
In-Built Tank Purifiers:
- Pros: Continuous water supply, especially during power cuts.
- Cons: Potential for bacterial growth if not cleaned regularly.
Direct Dispensers:
- Pros: Fresh, purified water directly from the source.
- Cons: Requires constant water supply.
Booster Pump: A Necessary Addition?
A booster pump can increase water pressure, especially in areas with low water pressure. If you experience low water pressure, a purifier with a booster pump can be beneficial.
Maintenance and Servicing
RO Purifiers:
- Regularly replace:
- Sediment filter (every 3-6 months)
- Carbon filter (every 6-12 months)
- RO membrane (every 12-24 months)
- Clean the storage tank every 3-6 months.
UV Purifiers:
- Replace the UV lamp every 6-12 months.
- Clean the UV chamber regularly.
By understanding the nuances of RO and UV technologies, you can make an informed decision about the best water purifier for your needs. Consider factors like water quality, budget, and lifestyle to select the right purifier for your home.